
They form a ring in between the membranes, and begin to expand outwards. The fontanelles contain connective tissue stem cells, which form into osteoblasts, which secrete calcium phosphate into a matrix of canals. On a baby, those spots are known as fontanelles. Ossification is started by the formation of layers of undifferentiated connective tissue that hold the area where the flat bone is to come. The intervening cancellous tissue is called the diploë, and this, in the nasal region of the skull, becomes absorbed so as to leave spaces filled with air–the paranasal sinuses between the two tables.

In the cranial bones, the layers of compact tissue are familiarly known as the tables of the skull the outer one is thick and tough the inner is thin, dense, and brittle, and hence is termed the vitreous (glass-like) table. In an adult, most red blood cells are formed in flat bones. These bones are composed of two thin layers of compact bone enclosing between them a variable quantity of cancellous bone, which is the location of red bone marrow.
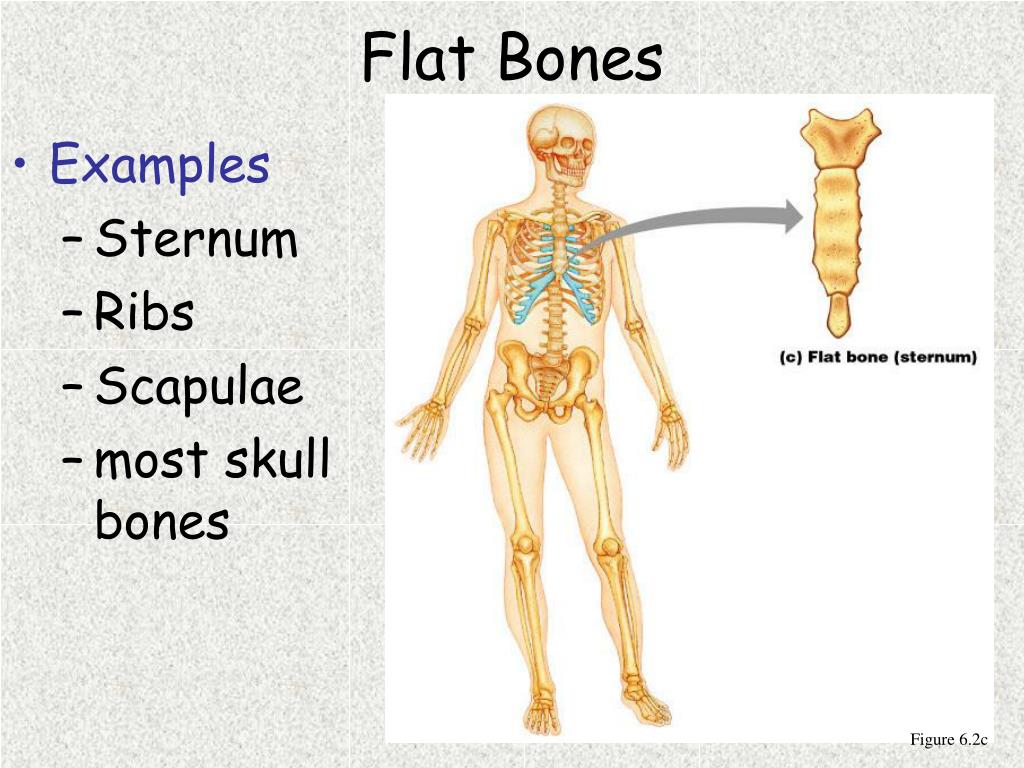
The flat bones are: the occipital, parietal, frontal, nasal, lacrimal, vomer, hip bone (coxal bone), sternum, ribs, and scapulae. These bones are expanded into broad, flat plates, as in the cranium ( skull), the ilium ( pelvis), sternum and the rib cage. Flat bones are bones whose principal function is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
